Rioters have attacked bank ATMs and blocked roads in three Nigerian cities as anger spilled on the streets over a scarcity of cash, just days before the country’s general election.
Nigeria has been struggling with a shortage in physical cash since the central bank began to swap old bills of the local naira currency for new ones, leading to a shortfall in banknotes.
Banks have limited access to cash for withdrawals because of a scarcity of the new notes, and some businesses refuse to accept old naira, causing huge queues, angering customers and disrupting businesses.
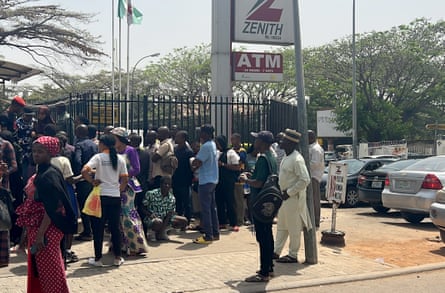
The unrest in the south-western city of Ibadan, and Benin City and Delta State in southern Nigeria, came days before Nigeria holds elections on 25 February to decide on a successor to the president, Muhammadu Buhari, who will step down after two terms.
Police in Delta State said “unguided youths/miscreants in the name of protests” set two banks and two vehicles on fire.
“We have arrested nine suspects so far. Some persons will still call this protest,” state police spokesperson Bright Edafe wrote on Twitter.
The Channels Television news station shared on its Twitter account a video of young men burning tyres in the streets on the outskirts of the city of Warri in Delta State.
In Benin City, protests broke out after police stopped “hoodlums” from attacking the local office of the central bank, according to the Edo State governor’s spokesperson, Crusoe Osagie.
“The hoodlums then started attacking and vandalising banks. They also blocked roads and forced businesses to close,” he said.
But he blamed the unrest on politically motivated actions by the ruling All Progressives Congress (APC) party, taking advantage of discontent to sow chaos in the opposition Peoples Democratic party (PDP)-governed state.
“Although the people are dissatisfied with the naira scarcity, the APC capitalised on the discontentment and instigated hoodlums and thugs to cause violence in the city,” Osagie said.
The APC did not immediately respond. But the APC and PDP have repeatedly traded accusations over the cash shortages during campaigning for next week’s election.
There were no immediate reports of deaths or injuries in Wednesday’s unrest.
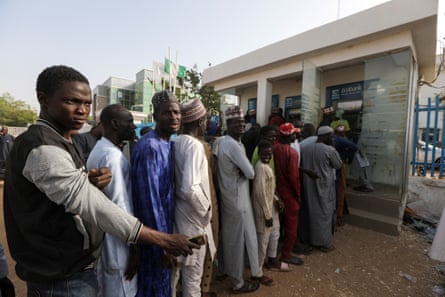
Angry customers also burned tyres and blocked streets in Ibadan, police and residents said. Oyo State police said protests broke out in some parts of Ibadan, the state capital, early on Wednesday, but were soon brought under control.
after newsletter promotion
“There were pockets of protest this morning by some aggrieved bank customers,” said spokesperson Adewale Osifeso.
Local residents said the unrest started in the Dupe, Mokola, Ogunpa, Apata and Iwo Road areas when angry bank customers began protesting because they could not access their money or change old notes to new ones.
“Major roads were blocked while banks, shops and other businesses were shut,” said a local journalist, Remi Feyisipo.
The protest on Wednesday followed riots last week in the city where two people were killed in clashes, according to local media.

Tensions have flared in Nigeria since the central bank set a February deadline for depositors to change old notes, leaving many people cashless and frustrated.
Many people working in the informal economy and in transport in Nigeria use cash for transactions rather than banking apps.
The central bank said the policy was aimed at mopping up excess and counterfeit naira from the system as well as discouraging cash ransom payments to kidnappers and bandits. The policy was also to promote cashless transactions by limiting the use of cash for businesses.
But some state governments have taken the central bank to court, seeking an order to suspend the policy and allow Nigerians to use both the old and new notes until the banks are able to provide enough cash.
Two weeks ago, riots also erupted in northern Nigeria’s largest city of Kano during a visit by Buhari, who has promised to look into the cash and petrol shortages.










